FIPS 140-2
Validate your product to meet Regulated Industry and Government requirements for cryptography

FIPS 140-2
Validate your product to meet Regulated Industry and Government requirements for cryptography
What Is FIPS 140-2?
The Federal Information Processing Standard 140-2 (FIPS 140-2) is a U.S. and Canadian co-sponsored security standard for hardware, software, and firmware solutions. In U.S. government procurement, all solutions that use cryptography must complete FIPS 140-2 validation to ensure end users receive a high degree of security, assurance, and dependability.
Are you being asked to support FIPS 140-2? Corsec can help, from analyzing your business drivers, to reviewing your product architecture; our team can help educate you on the standard and detail how to quickly address your requirements.
FIPS Inside & FIPS Compliance
Corsec details the differences between FIPS 140-2 Validation, FIPS Compliant, and FIPS Inside.
Your customer requests, timelines, and product will all have an influence on which approach is best suited for your company. Review the white-paper to learn more.
FIPS Inside & FIPS Compliance
Corsec details the differences between FIPS 140-2 Validation, FIPS Compliant, and FIPS Inside.
Your customer requests, timelines, and product will all have an influence on which approach is best suited for your company. Review the white-paper to learn more.
The Standard: FIPS 140-2
 The use of FIPS 140-2 validated products is mandated by Section 5131 of the Information Technology Management Reform Act of 1996.
The use of FIPS 140-2 validated products is mandated by Section 5131 of the Information Technology Management Reform Act of 1996.
 All products sold into U.S. federal agencies are required to complete FIPS 140-2 validation if they use cryptography in security systems that process Sensitive But Unclassified (SBU) information.
All products sold into U.S. federal agencies are required to complete FIPS 140-2 validation if they use cryptography in security systems that process Sensitive But Unclassified (SBU) information.
 Security requirements are outlined in full within the NIST FIPS 140-2 PUB.
Security requirements are outlined in full within the NIST FIPS 140-2 PUB.
The Requirements: Security & Levels
FIPS 140-2 contains eleven Derived Test Requirements (DTRs) that detail the requirements that must be provided to demonstrate conformance to the standard. Each section also describes the methods that the testing lab will take to test the module.
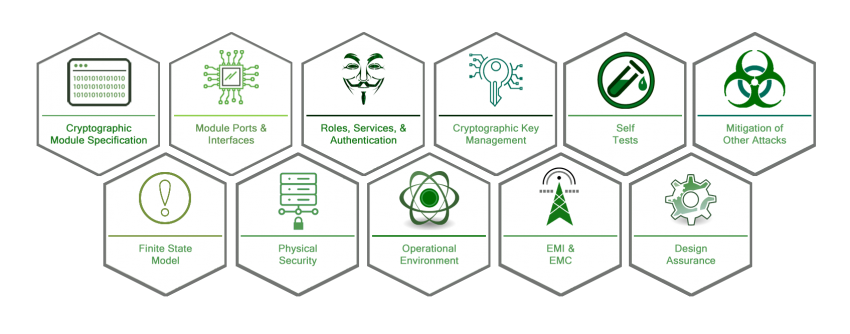
Within each of the eleven sections, there are four increasing qualitative security levels. At each level, greater amounts of evidence and engineering are required of the product in order to show compliance with the standard:
